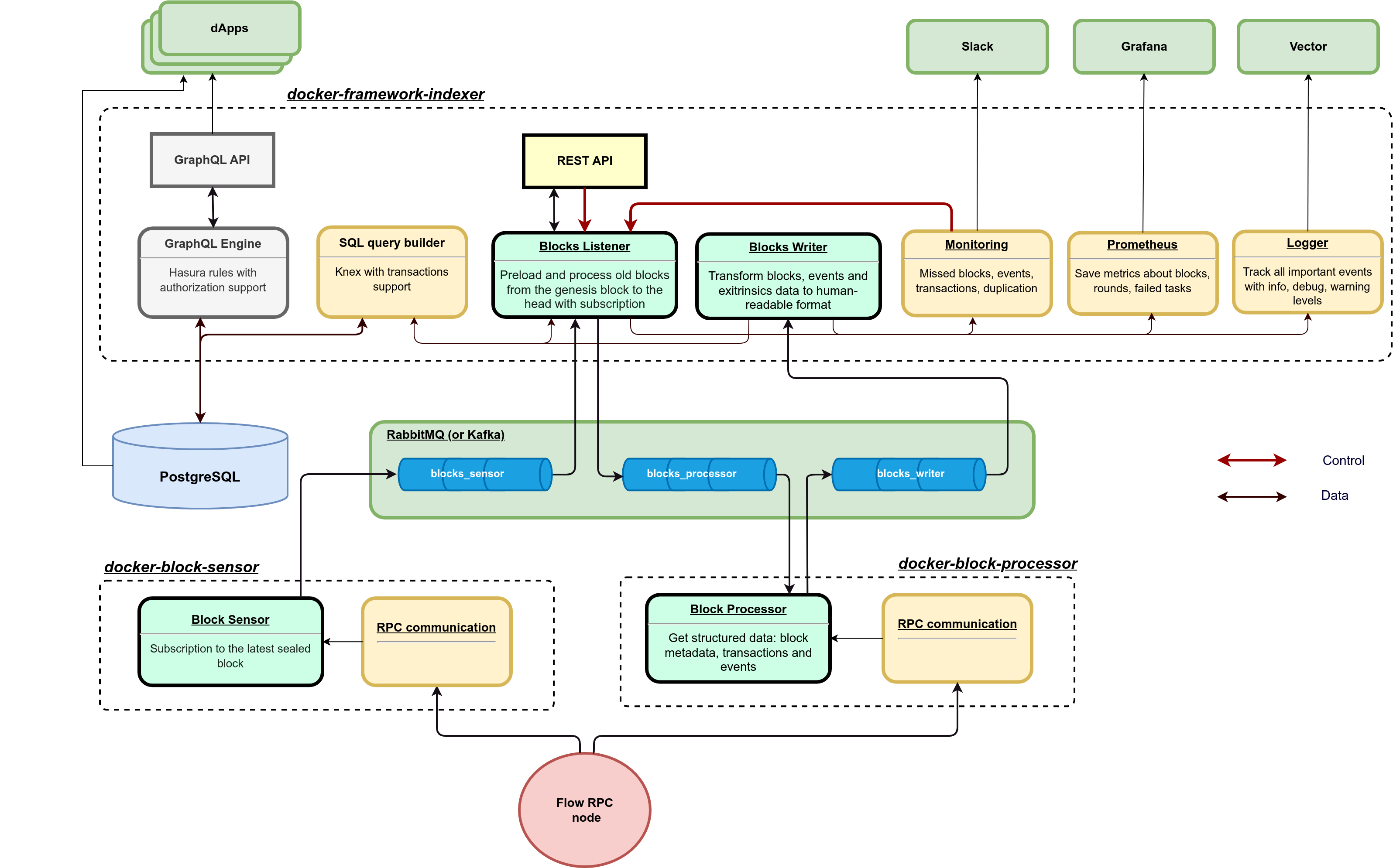
Flow Indexer is the first open-source data warehouse designed to provide application-specific data for the Flow blockchain. Its purpose is to reduce costs and simplify the process of building wallets, dashboards, explorers, and dApps that interact with Flow blockchain.
- Real-time data (with a maximum delay of 20 seconds for a block to appear in the database).
- High-speed extraction (up to 1000 blocks per hour for one instance with 1 CPU and 200MB RAM).
- High scalability (100 instances can process 100K blocks per hour).
- High-speed access to extracted data (up to 10 thousand rows per second).
- Docker-compose in-house setup in 5 seconds.
- BlockSensors: 1cpu, 200MB
- BlockProcessor: 1-100cpu, 200MB
- IndexerFramework: 1cpu, 500MB
- PostgreSQL: 1cpu, 1GB
- RabbitMQ: 1cpu, 300MB
1. Update package:
sudo apt update
2. Install package for HTTPS:
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
3. Add GPG-key for Docker:
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
4. Add repository for Docker:
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bionic stable"
5. Update package:
sudo apt update
6. Switch to Docker repository and install:
apt-cache policy docker-ce
7. Install Docker:
sudo apt install docker-ce
8. Check installation:
sudo systemctl status docker
Output info:
docker install ubuntu
Docker install Ubuntu
9. Check Docker image:
docker run hello-world
You must see «Hello from Docker!»
10. Install docker compose
sudo apt install docker-compose
11. Check docker-compose
docker-compose --version
Output info:
docker-compose version 1.20.1, build 1719ceb
Create the .env file:
cp .env.sample .envSpecify the RPC URL in the .env file. For example:
RPC_URI=https://rest-mainnet.onflow.orgSpecify the block ID from which you want to start the sync. For example:
START_BLOCK_ID=56000000Start the Docker containers:
docker-compose up -d
If you want to run 30 Block Processor instances then run it like
docker-compose up -d --scale flow_block_processor=30
├── db: Schema to set up a PostgreSQL database.
├── db-data: External Docker volume for PostgreSQL data.
├── docker-compose.yml: Definition of all containers (DB, RabbitMQ, BlockSensors, BlockProcessors, IndexerFramework, etc.).
├── framework: Indexer framework for controlling the indexing process (language: TypeScript).
│ ├── Dockerfile: Common Docker rules for building the Indexer Framework container.
│ └── src
│ ├── index: Main application.
│ ├── environment: Environment definition with default values.
│ ├── loaders
│ │ ├── database: PostgreSQL initializer using the Knex library.
│ │ ├── express: Express initializer for the REST API.
│ │ ├── logger: Pino logger initializer.
│ │ ├── prometheus: Prometheus metrics initializer for Grafana.
│ │ └── rabbitmq: RabbitMQ queue initializer.
│ ├── models: Database models.
│ └── modules
│ ├── index: Modules initializer depending on the MODE (specified in docker-compose.yml).
│ ├── BlockListener: Initial preloader and finalized block processor.
│ │ ├── index: Module initializer.
│ │ ├── controller: REST API endpoints.
│ │ ├── service: Base module logic (get message from BlockSensor, check it, and send it to BlockProcessor queue).
│ │ └── helpers
│ │ └── database: Methods for getting/saving data in the database.
│ ├── BlockWriter: Get block data structure from BlockProcessor and write it to the database.
│ └── Monitoring: Check missing blocks and tasks.
└── src: Main containers for fetching block data from the RPC node.
├── block-sensor: Python module for fetching the latest block height.
│ ├── Dockerfile: Common Docker rules for building the Python container.
│ └── sensor.py: Get the latest block height from the RPC node and send it to the RabbitMQ queue.
└── block-processor: Python module for getting block data, transactions, and events from the RPC node.
├── Dockerfile: Common Docker rules for building the Python container.
└── processor.py: Main script for getting structured block data from the RPC node.
The database schema is described in the ./db/init.sql. This file is used as the entrypoint SQL when Postgres is started using the ./db/Dockerfile defined in the ./docker-compose.yml file.
The schema includes the following tables:
blocks: This table stores information about blocks, including block height, block ID, parent ID, block time, and parent voter signature.
events: This table stores information about events, including block height, event ID, transaction ID, transaction index, event index, type, and payload.
transactions: This table stores information about extrinsics, including block height, block ID, transaction ID, script, arguments, reference block ID, gas limit, payer, proposal key, authorizers, payload signatures, envelope signatures, execution, status, status code, error message, and computation used.
processing_tasks: This table stores information about processing tasks, including network ID, entity, entity ID, status, collection unique ID, start time, finish time, data, attempts, and a unique identifier (row_id).
processing_state: This table stores information about the processing state, including network ID, entity, entity ID, and a unique identifier (row_id). It also has a constraint to ensure a unique combination of entity and network ID.
processing_metrics: This table stores information about processing metrics, including delay_time_ms, process_time_ms, missed_count, duplicates_count, rpc_sync_diff_count, memory_usage_mb, not_processed_count, and restart.
Please refer to the ./db/init.sql file for the detailed schema definition.
These metrics provide insights into the speed, data quality, and system performance of the indexer.
- Speed:
- delay_time_ms: The time it takes for a block to appear in the blockchain and be found in the database, measured in milliseconds.
- process_time_ms: The time it takes to process a block, measured in milliseconds.
- Data Quality:
- missed_count: The number of missed blocks, indicating blocks that were not successfully processed or recorded.
- duplicates_count: The number of duplicate records, indicating instances where the same data has been recorded multiple times.
- rpc_sync_diff_count: The difference between the data in the RPC (Remote Procedure Call) and the data stored in the database.
- System:
- memory_usage_mb: The amount of memory used for processing each task, measured in megabytes.
- not_processed_count: The number of unprocessed tasks, indicating tasks that have not been completed.
- restart: The count of indexer restarts, indicating the number of times the indexer has been restarted.
Check indexer health
responds with {"status":"live"} if the system is healthy.
Success.
Request not authenticated due to missing, invalid, authentication info.
A specified resource is not found.
Unknown server error.
- 200
- 401
- 404
- 500
{- "status": "live"
}Restart unprocessed blocks
Restarts the extraction of all unprocessed blocks. Increase the memory of the BlockProcessor instance before calling this method if there were problems with block data extraction.
Success.
Request not authenticated due to missing, invalid, authentication info.
A specified resource is not found.
Unknown server error.
- 200
- 401
- 404
- 500
{- "status": "success"
}Process specified block
Manually processes the specified blockId.
Success.
Request not authenticated due to missing, invalid, authentication info.
A specified resource is not found.
Unknown server error.
- 200
- 401
- 404
- 500
{- "status": "success"
}Process specified blocks range
Manually processes a range of blocks from startBlockId to endBlockId.
Success.
Request not authenticated due to missing, invalid, authentication info.
A specified resource is not found.
Unknown server error.
- 200
- 401
- 404
- 500
{- "status": "success"
}